搜索文档
介绍
在 Java 中所有类均继承 Object 类。
clone() 方法
作用
克隆一个对象,返回值是 Object 类型。
用法
若一个类型的对象想实现 clone 方法,需要遵循一下几点:
- 类要实现 Cloneable 接口。
- 在类中充血 clone 方法。
- 使用 clone 方法创建对象(这要要使用异常处理)
代码实现
Student 类
javapublic class Student implements Cloneable { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }Demo 类
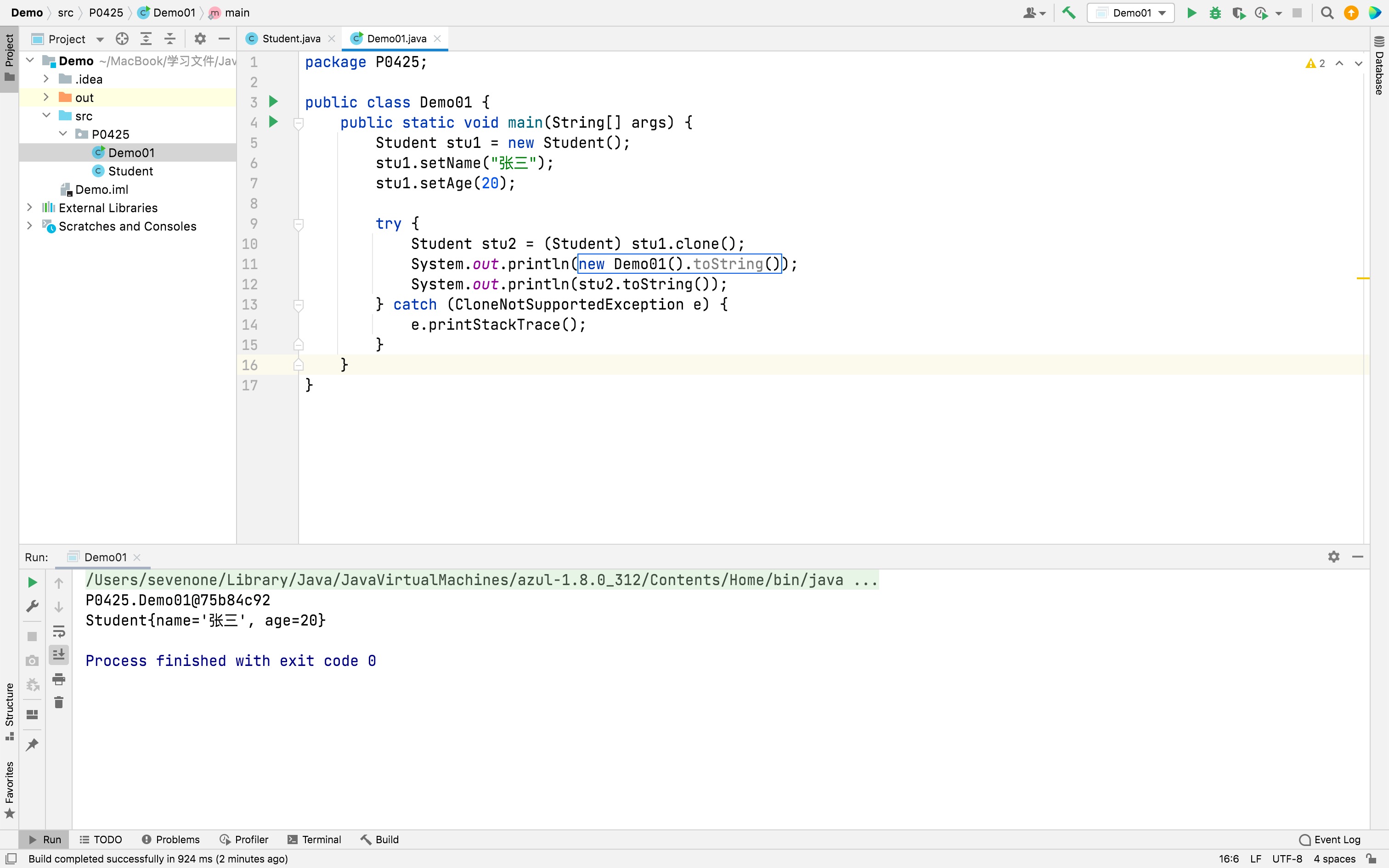
javapublic class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu1 = new Student(); stu1.setName("张三"); stu1.setAge(20); try { Student stu2 = (Student) stu1.clone(); System.out.println(stu2.getName()); System.out.println(stu2.getAge()); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }运行结果
equals() 方法
作用
- 判断两个对象的内存地址是否一样,同 ==。
- 开发过程中可能会被重写,并不是每次都判断对象的内存地址,还有可能是判断对象的数据是否一样。
代码实现
Student 类同上。
Demo 类
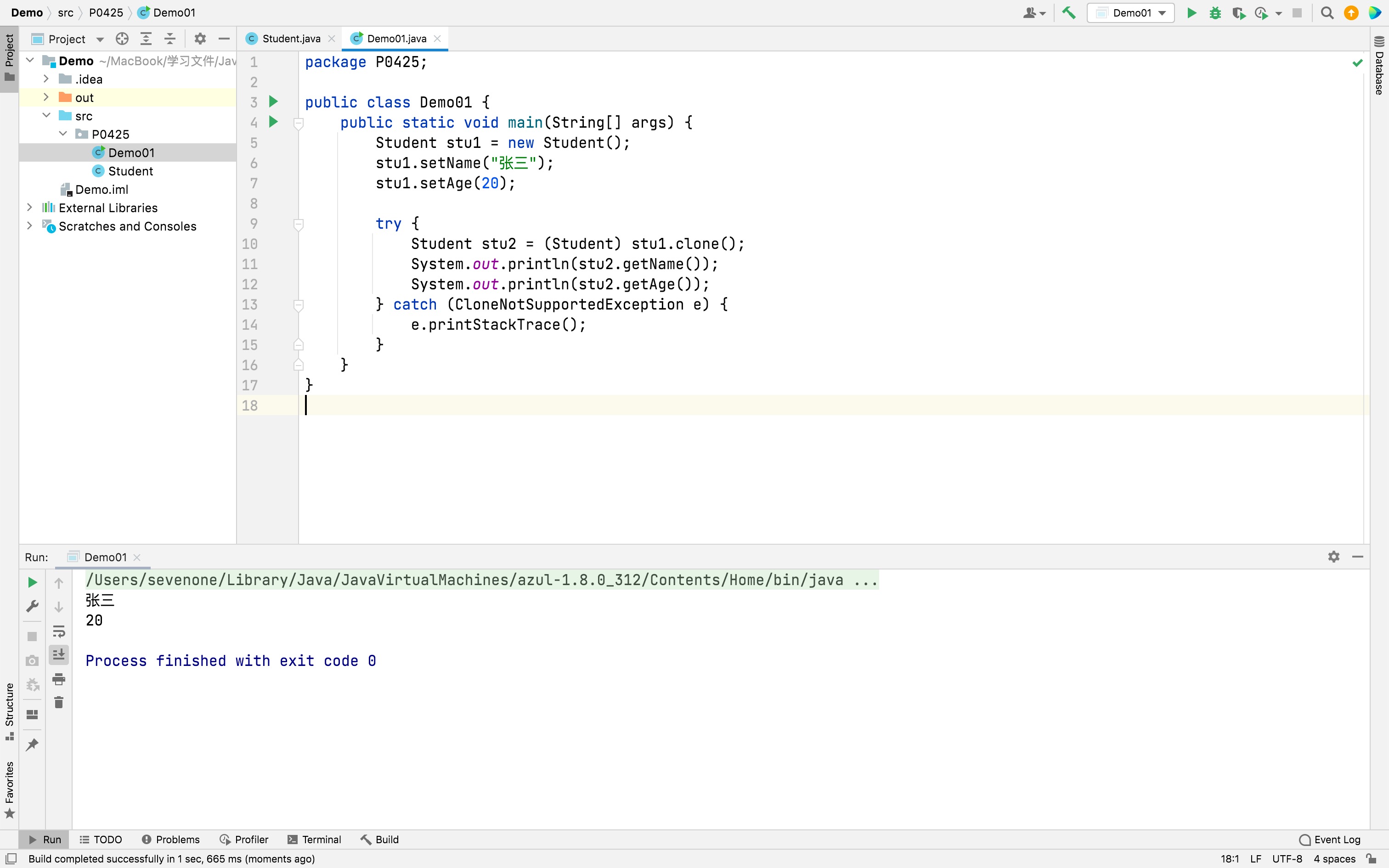
javapublic class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu1 = new Student(); stu1.setName("张三"); stu1.setAge(20); try { Student stu2 = (Student) stu1.clone(); Student stu3 = stu2; System.out.println(stu2.equals(stu1)); System.out.println(stu2.equals(stu3)); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }运行结果
toString() 方法
作用
- 将数据转化为字符串。
- 当输出一个对象时,首先找到对象的内存地址,再调用 toString 方法转成字符串后输出。
代码实现
在 Student 类中重写 toString 方法
java@Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; }Demo 类
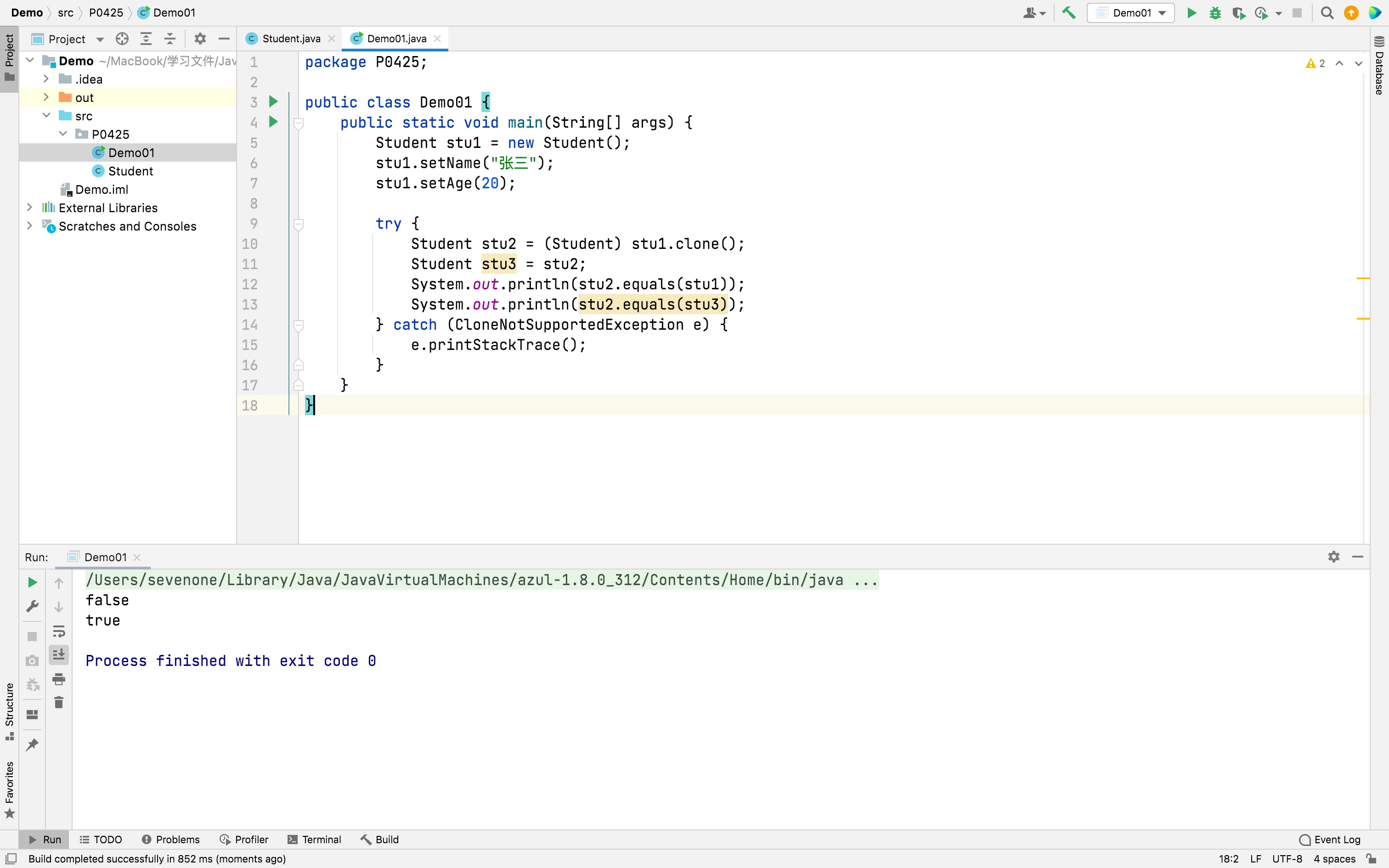
javapublic class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu1 = new Student(); stu1.setName("张三"); stu1.setAge(20); try { Student stu2 = (Student) stu1.clone(); System.out.println(new Demo01().toString()); System.out.println(stu2.toString()); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }运行结果