搜索文档
概念
- 在父类中定义了一个方法 fun,若这个方法不满足子类的需求,在子类中可以对这个方法进行重写。
- 重写父类方法需要注意以下几点(下面 fun0 表示父类方法,fun1表示子类方法)
- fun1 的方法名、形参列表必须与 fun0 相同。
- fun1 的返回值要小于 fun0 的返回值。
- fun1 的访问权限大于 fun0 的访问权限。
重写
需求
- 定义一个人类,属性(无)方法(play)
- 定义一个继承人类的学生类,属性(无)方法(play)
代码实现
java
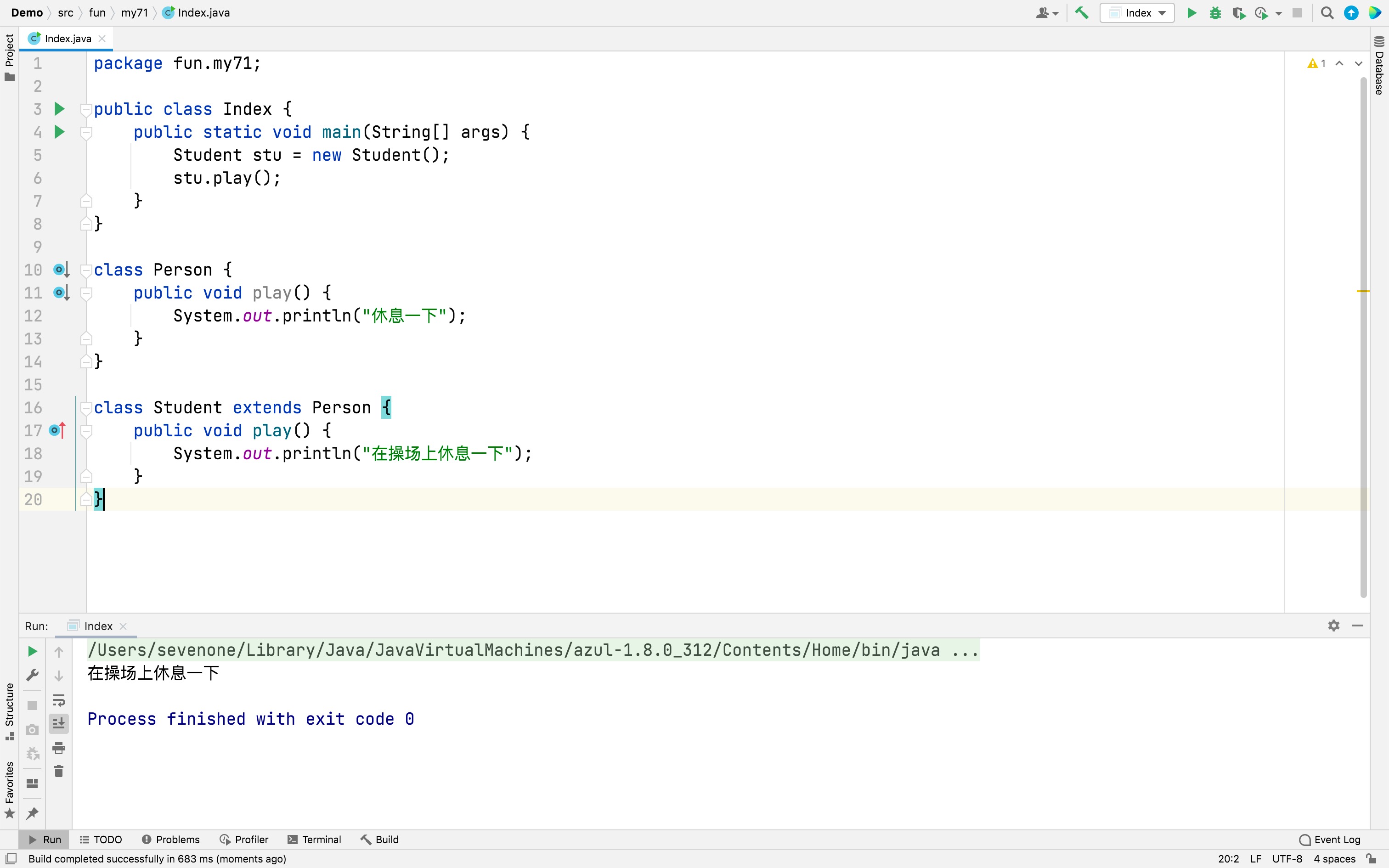
package fun.my71;
public class Index {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.play();
}
}
class Person {
public void play() {
System.out.println("休息一下");
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public void play() {
System.out.println("在操场上休息一下");
}
}
返回值问题
要求子类中方法返回值要小于父类中方法的返回值。
代码
javapackage fun.my71; public class Index { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu = new Student(); stu.play(); } } class Person { public Person play() { return new Person(); } } class Student extends Person { public Student play() { return new Student(); } }注:这种情况是可以的,因为 Student 类继承 Person 类,所以 Student 类小于 Person 类,父类 play 方法返回值是一个 Person 类的对象,而子类的 play 方法返回的是一个 Student 类的对象,所以这样是可以的。
javapackage fun.my71; public class Index { public static void main(String[] args) { Student stu = new Student(); stu.play(); } } class Person { public Person play() { return new Person(); } } class Student extends Person { public Object play() { return new Object(); } }注:这种情况显然不行,因为 Person 没有继承任何类,所以默认父类是 Object,也就是说 Person 小于 Object,再看返回值,明显不满足返回值要求。
重写 equals 方法
java
package fun.my71;
public class Index {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu1 = new Student(1001,"张三",21);
Student stu2 = new Student(1002,"李四",23);
System.out.println(stu1.equals(stu2));
}
}
class Student {
int id;
String name;
int age;
public Student(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean equals(Student obj) {
return this.id == obj.id;
}
}